Microscopy & Staining
Pre-Lecture Quiz
1) What is the subject of study in histology?
(A) Cells
(B) Diseases
(C) Organs
(D) Tissues
-
(A) Cells – Cytology is the study of cells
(B) Diseases – Pathology is the study of diseases
(C) Organs – Study of organs is at the anatomic level
(D) Tissues – Histology is the study of tissues
3) Which circle in the image outlines a cell?
(A) Circle #1
(B) Circle #2
(C) Circle #3
-
(A) Circle #1 encircles the nucleus of a cell
(B) Circle #2 encircles the nucleus of a cell
(C) Circle #3 encircles the entire cell
5) Which microscopy has the highest magnification power?
(A) Light microscopy
(B) Phase contrast microscopy
(C) Fluorescence microscopy
(D) Transmission electron microscopy
(E) Scanning electron microscopy
-
(A) Light microscopy - up to 1000x magnification
(B) Phase contrast microscopy – magnification power is typically less than A
(C) Fluorescence microscopy – similar magnification power as light
(D) Transmission electron microscopy – provides the highest magnification (1,000,000x)
(E) Scanning electron microscopy – up to 30,000x magnification
2) What is the most commonly used staining technique in histology?
(A) H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin)
(B) Immunofluorescence
(C) Immunohistochemistry
(D) Periodic acid Schiff
-
(A) H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin) is the most commonly used staining
(B) Immunofluorescence is used to visualize specific protein expression using fluorescent tags
(C) Immunohistochemistry is similar to immunofluorescence but uses chromogenic tags
(D) Periodic acid Schiff is used to visualize areas of high carbohydrate concentration
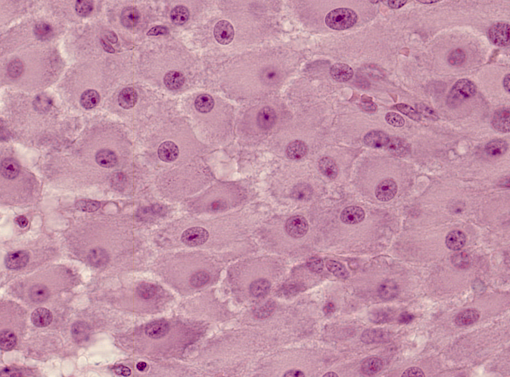
4) Which dye is responsible for the pink appearance of the cells in this image?
(A) Eosin
(B) Hematoxylin
(C) Periodic Acid Schiff
(D) Trichrome
-
(A) Eosin, a negatively charged acidic dye, stains positively charged proteins in the cytoplasm
(B) Hematoxylin – a positively charged basic dye stains negatively charged acid molecules
(C) Periodic acid Schiff reacts with carbohydrate moieties
(D) Trichrome stains collagen fibers