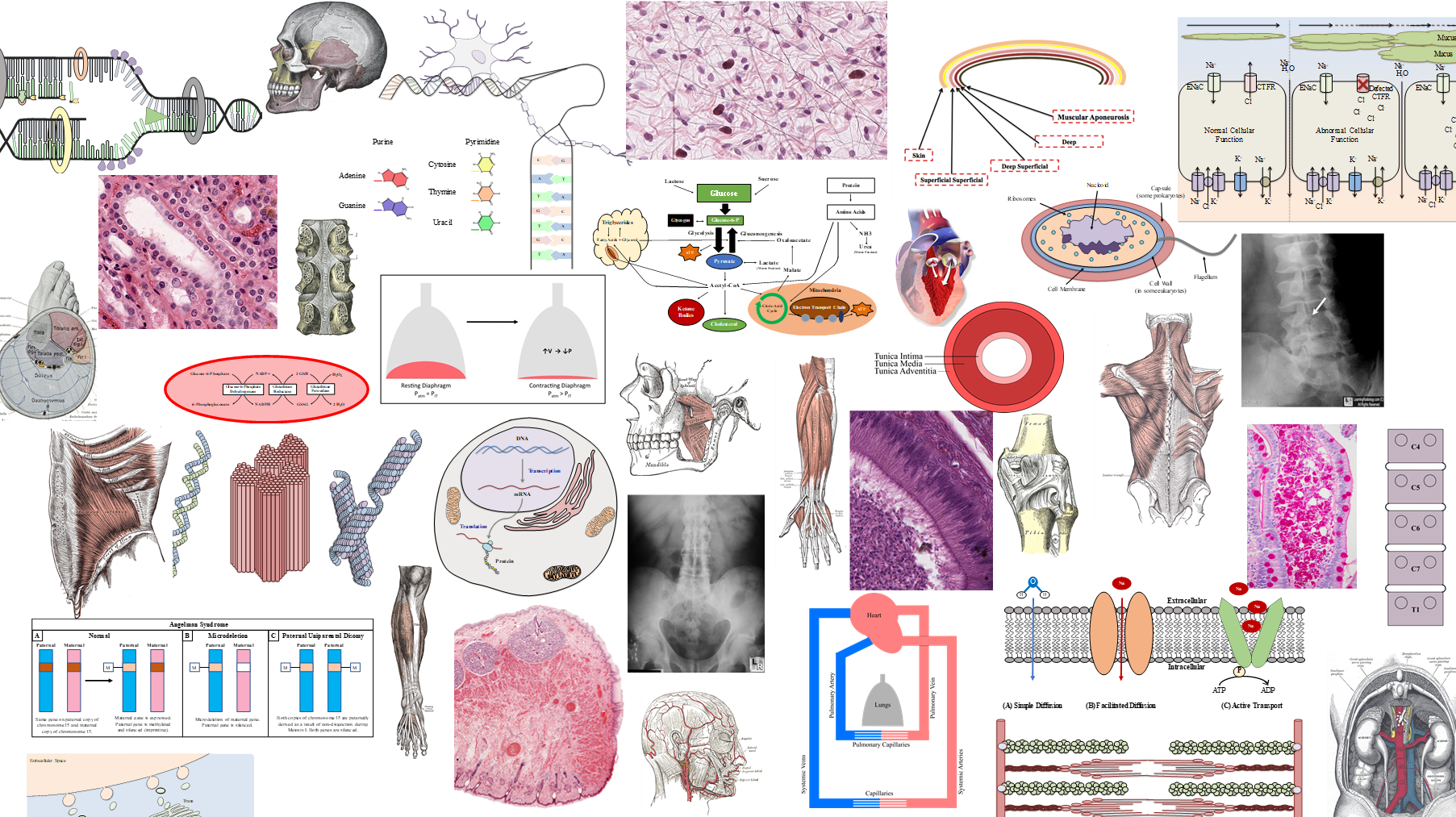
Microscopy & Staining
Post-Lecture Quiz
1) Which staining technique is best suited to visualize two proteins of interest on the same tissue section?
(A) H&E
(B) Immunofluorescence
(C) Immunohistochemistry
(D) Periodic acid Schiff
-
(A) Circle #1 encircles the nucleus of a cell
(B) Circle #2 encircles the nucleus of a cell
(C) Circle #3 encircles the entire cell
-
(A) H&E – stain acidic & basic structures in the cell indiscriminately
(B) Immunofluorescence – using secondary antibodies with different fluorescence tags, more than one protein may be tagged in a single tissue slide
(C) Immunohistochemistry – the chromogen on the secondary antibodies turn one color (brown) thus one can’t distinguish different protein expressions in a single tissue slide
(D) Periodic acid Schiff – this turns all carbohydrate-rich regions of the tissue magenta indiscriminately
3) Which circle in the image outlines a cell?
(A) Circle #1
(B) Circle #2
(C) Circle #3
5) Which staining technique is best suited to visualize two proteins of interest on the same tissue section?
(A) H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin)
(B) Immunofluorescence
(C) Immunohistochemistry
(D) Periodic acid Schiff
-
(A) H&E – stain acidic & basic structures in the cell indiscriminately
(B) Immunofluorescence – using secondary antibodies with different fluorescence tags, more than one protein may be tagged in a single tissue slide
(C) Immunohistochemistry – the chromogen on the secondary antibodies turn one color (brown) thus one can’t distinguish different protein expressions in a single tissue slide
(D) Periodic acid Schiff – this turns all carbohydrate-rich regions of the tissue magenta indiscriminately
7) Which step in histotechnology stops tissues from degradation?
(A) Embedding
(B) Fixation
(C) Processing
(D) Sectioning
(E) Staining
-
(A) Embedding – processed tissue is placed in a paraffin block
(B) Fixation – fixative such as formaldehyde denatures proteins and stops tissue degradation
(C) Processing – fat and water in the tissue are replaced with paraffin
(D) Sectioning – tissues in paraffin block are thinly sectioned
(E) Staining – thinly sectioned tissues are stained
2) Which circle in the image outlines a cell?
(A) Circle #1
(B) Circle #2
(C) Circle #3
-
(A) Circle #1 is a nucleus of a cell, the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in the nucleus stain well with hematoxylin which has blue to purple hue
(B) Circle #2 is the cytoplasm of a large cell and is staining pink with eosin which stain positively charged, basic substances
(C) Circle #3 is an artifact
*The pale staining areas are rich with ground substance
4) To compare the amount of glycogen storage in the liver cells of starved vs. well-fed rats, which staining technique should be used?
(A) H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin)
(B) Immunofluorescence
(C) Immunohistochemistry
(D) Periodic acid Schiff
-
(A) H&E – stain acidic & basic structures in the cell indiscriminately
(B) Immunofluorescence – using secondary antibodies with different fluorescence tags, more than one protein may be tagged in a single tissue slide
(C) Immunohistochemistry – the chromogen on the secondary antibodies turn one color (brown) thus one can’t distinguish different protein expressions in a single tissue slide
(D) Periodic acid Schiff – this turns all carbohydrate-rich regions of the tissue magenta indiscriminately
6) Which structure is a form of ground substance?
(A) Collagen
(B) Glycosaminoglycans
(C) Reticular fibers
(D) Plasma
-
(A) Collagen - a type of fiber
(B) Glycosaminoglycans – one form of ground substance, the others are proteoglacans, and glycoproteins
(C) Reticular fibers are a type of fibers
(D) Plasma is the fluid component of blood which is similar to the interstitial fluid


