Microscopy & Staining
Post-Lecture Quiz
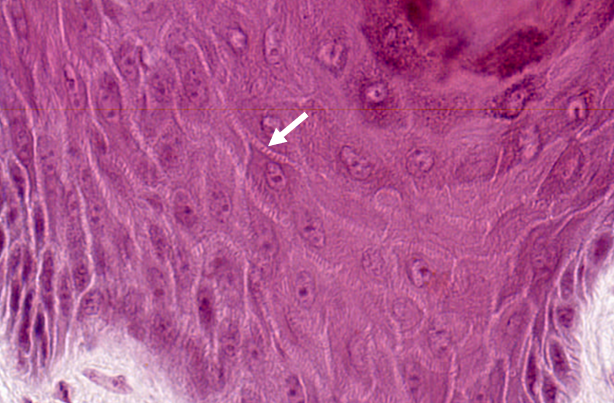
1) Which part of the body is this skin section most likely taken from?
(A) Scalp
(B) Face
(C) Chest
(D) Palm
(E) Thigh
-
(A) Scalp – Skin over scalp is thin skin, this tissue section is thick skin.
(B) Face – Skin over face is thin skin, this tissue section is thick skin.
(C) Chest – Skin over chest is thin skin, this tissue section is thick skin.
(D) Palm – This section is thick skin which is found in the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.
(E) Thigh – Skin over thigh is thin skin, this tissue section is thick skin.
3) Which layer of the epidermis connects to the basal lamina via hemidesmosomes?
(A) Stratum corneum
(B) Stratum lucidum
(C) Stratum granulosum
(D) Stratum spinosum
(E) Stratum basale
-
(A) Stratum corneum
(B) Stratum lucidum
(C) Stratum granulosum
(D) Stratum spinosum
(E) Stratum basale – Anchors to the basal lamina via hemidesmosomes connecting to integrins within the basal lamina, which serves to anchor the epidermis to the dermis.
5) The gland in this slide carries out what type of secretion?
(A) Apocrine
(B) Merocrine
(C) Holocrine
-
(A) Apocrine – Small regions of cytoplasm and surrounding cell membrane containing the secretion bud off. None of the glands in the skin carry out apocrine secretion.
(B) Merocrine – Secretion via exocytosis. Carried out by both eccrine and apocrine sweat glands.
(C) Holocrine – This is a sebaceous gland which carries out holocrine secretion, which occurs when the cell ruptures releasing the secretion into the lumen of the gland.
2) The white arrow is pointing to which of the following structures?
(A) Gap junctions
(B) Melanosomes
(C) Bundles of keratin filaments
(D) Langerhans cell
-
(A) Gap junctions – Gap junctions are not present between keratinocytes.
(B) Melanosomes – Melanosomes are vesicles containing bundles of melanin and do not demonstrate a spiny appearance on light microscopy as shown by the arrow in this slide.
(C) Bundles of keratin filaments – The arrow is pointing to the stratum spinosum layer of the epidermis, which is named for spiny appearance of the keratinocytes. The spiny appearance is a result of the bundles of keratin filament (tonofilaments) found within cytoplasmic extensions that are associated with desmosomes linking adjacent keratinocytes.
(D) Langerhans cell – Although Langerhans cells are usually found in the stratum spinosum layer, they are macrophages with the characteristic dense, basophilic, indented nucleus with a pale cytoplasm.
4) Individuals with darker skin color have which of the following compared to individuals with lighter skin color?
(A) Higher number of melanocytes
(B) Slower rate of melanin production
(C) Slower rate of melanosome degradation
(D) Less aggregation of melanosomes within keratinocytes
-
(A) Higher number of melanocytes – Number of melanocyte cells is equal among all races.
(B) Slower rate of melanin production – Individuals with darker skin have higher rates of melanin production.
(C) Slower rate of melanosome degradation – Individuals with darker skin have slower rate of melanosome degradation, allowing for more aggregation of melanosomes.
(D) Less aggregation of melanosomes within keratinocytes – Individuals with darker skin have more aggregation of melanosomes.
6) What specific sensation is this structure responsible for?
(A) Tactile sensation
(B) Light touch
(C) Sustained stretching
(D) Sustained pressure
-
(A) Tactile sensation – Meissner’s corpuscle. These receptors are found in the dermal papilla at the epidermis-dermis junction.
(B) Light touch – Merkel’s corpuscle.
(C) Sustained stretching – Ruffini corpuscle.
(D) Sustained pressure – Pacinian corpuscle.